Buy URB-597 Online
$200.00 – $2,600.00Price range: $200.00 through $2,600.00
100% Discreet Shipping. Get 20% Off On Crypto Purchase
URB597 is a potent and selective inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), the enzyme that hydrolyzes anandamide
BUY URB-597 ONLINE
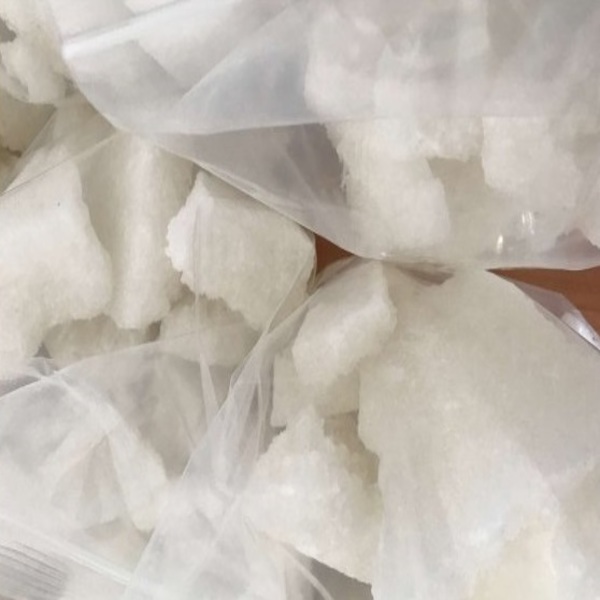
URB-597 (also known as KDS-4103) is a synthetic compound that acts as a fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor. FAAH is an enzyme in the brain and body that breaks down anandamide, a naturally occurring endocannabinoid (a chemical similar to THC, the active compound in cannabis). Buy URB-597 online.
How It Works
URB-597 blocks FAAH, which prevents the breakdown of anandamide.
As a result, anandamide levels increase in the brain and body — indirectly stimulating cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) and producing effects similar to mild cannabis activation, but without THC or direct receptor binding. Buy URB-597 online
Content Overview
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical name | [3-(3-carbamoylphenyl)phenyl] N-cyclohexylcarbamate |
| Synonyms | KDS-4103, URB597 |
| Molecular formula | C₂₀H₂₂N₂O₃ |
| Molecular weight | 338.4 g/mol |
| Chemical class | Carbamate derivative |
| Type | Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor |
| Physical form | Off-white to white crystalline powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol, and organic solvents; low water solubility |
| Melting point | ~86–88 °C |
URB-597 For Sale
Active Content
- The active chemical in URB-597 is the FAAH-inhibiting compound itself (no mixtures or plant materials).
- It does not contain cannabinoids (like THC or CBD) — instead, it acts indirectly on the body’s endocannabinoid system by preserving anandamide.
- In research-grade material, purity typically ranges from ≥98 % to ensure consistent enzyme inhibition activity.
Pharmacological Content
Target enzyme: Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH).
Action: Irreversible inhibition.
Effect: Elevates anandamide and oleamide levels.
Resulting impact: Analgesic, anxiolytic, antidepressant-like, and anti-inflammatory effects (in animals). Buy URB-597 online
Important Notes
- URB-597 is a pure synthetic research compound, not a blend or formulation.
- Sold only for laboratory and academic research — not for human or veterinary use.
- Often stored in powder form at low temperature (−20 °C) to maintain stability.
| Quantity | 1 Kg, 10 Grams, 100 Grams, 20 Grams, 50 Grams, 500 Grams |
|---|
Related products
Research Chemicals
Research Chemicals
Research Chemicals
Research Chemicals
Research Chemicals
Nembutal
Research Chemicals
Research Chemicals